Digital Wallets Security
Introduction to digital wallets
Digital wallet, also referred as "e-Wallet" allows people to perform electronic transactions without the need to have physical cards.
Not only does it allows to perform payment and transactions, but also is handy to store other identity documents such as loyalty card(s) within the wallet. It also eliminates the need to carry multiple physical cards.
Now as we have understood in simple words the meaning of digital wallets let us understand how do digital wallet transactions work.
Steps of a digital wallet transaction being performed
To use a digital wallet, the user needs to open the wallet application on mobile. To do this users can either use facial recognition, fingerprint identification, or PIN codes (based on the phone model and the configuration)
Post unlocking the application, the user next selects the stored payment method for use, as digital wallets allows to store multiple cards
There can be two type of transactions for digital wallets.
In-person purchases: Digital wallets use wireless and magnetic capabilities to transmit payment data from a mobile device to the payment device
Online purchases: The user selects a digital payment (such as payment via google pay/ apple pay etc.) and do the succeeding steps.
In person purchases happen via “Contactless” medium via the below technologies:
1. Near-field communication (NFC)
Near-field communication (NFC) is the most common contactless payments. These allows devices to transmit payment information to payment terminals in close proximity with mobile device and removing the need to have physical contact.
2. Magnetic secure transmission (MST)
Magnetic secure transmission (MST) is allows smartphones to emit an encrypted signal similar to the magnetic stripe on credit and debit cards to facilitate payments.
3. QR codes
Quick response (QR) codes offers another medium of payment (popular with UPI applications), which post scanning, facilitates payment.
Key features of digital wallets include:
1. Users can do a one-time setup in their digital wallet, eliminating the need to enter details such as PIN for each transaction
2. Payments are quicker and convenient via smartphones, tablets, or computers.
3. Security: Digital wallets use various security measures, such as encryption and authentication methods, to protect users' information.
Popular digital wallets include:
Apple Pay: Enables users to make payments using their iOS devices.
Google Pay: Enables users to make payments using Android devices.
Samsung Pay: Enables Samsung’s mobile users to pay via both NFC and traditional magnetic stripe card terminals.
All the above wallets having linked payment cards do not store any actual data or share it with the payment processor during transactions, which makes it highly secure.
The saved cards use a concept called "tokenization" which allows replacing confidential data against non-confidential data/ tokens. Think of it like a one way process where the the confidential data is used to create a token, however the inverse is not possible. These tokens are called EMVs.
These tokens are managed by "Token service providers" or TSPs which are registered with EMVco. (EuroPay, Mastercard, Visa) Ultimately these TSPs offer their tokenization services to "Token requestors" or TR to initiate the requests.
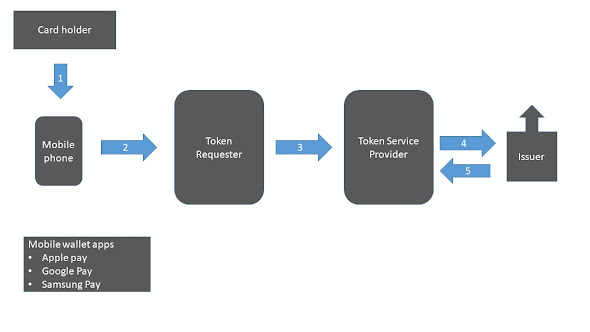
Let's see the process using a visual diagram
Card holder enters card details in the digital wallet application
The application sends data to Token Requestor (TR)
The TR send it ahead to Token Service Provider (TSP) which makes the request for generating a token
The TSP validates the cad details with the card issuing authority
The card details are linked with a token stored in a vault which is then shared with the digital wallet application.
For all transactions, now the mobile device is used for contactless payment which goes through the payment network which validates the generated TSP tokens and the issuer bank to complete the transaction.
Now let's understand how individual digital wallets work?
Apple Pay:
Apple Pay component security
Apple Pay has several components as part of its overall system to provide secure payment options
1. Secure Element (SE)
The Secure Element is an industry-standard, certified chip running the Java Card platform, which is compliant with financial industry requirements for electronic payments. This Secure Element IC and the Java Card platform are certified with the EMVCo Security Evaluation process.
2. NFC controller
The NFC controller handles Near Field Communication protocols and routes communication between the Application Processor and the Secure Element, and between the Secure Element and the point-of-sale terminal.
3. Secure Enclave
On apple devices with Touch ID, the Secure Enclave manages the authentication process and allows a payment transaction to proceed. On Apple Watch, the device must be unlocked, and the user must double-click the side button. This double-click is detected and passed directly to the Secure Element or Secure Enclave, where available, without going through the Application Processor.
4. Apple Pay servers
The Apple Pay servers manage the setup and provisioning of credit, debit, access cards etc. in Apple Wallet. The servers also manage the Device Account Numbers stored in the Secure Element. They communicate both with the device and with the payment network or card issuer servers. The Apple Pay servers are also responsible for re- encrypting payment credentials for payments within apps or on the web.
I have made a simple diagram to explain the process from the stage of setting up a card in Apple Pay all the way to transactions being performed
Similar to the above- Google pay and Samsung pay have similar functionalities and use the near same mechanism.
Source: Apple Pay Website, Wiki, Internet research




Hey nice blog,Thanks for this helpful information come back again for more interesting information. Keep it up! Network Security Providers
ReplyDeleteThe Apartment Entry Systems in the lobby allows you to select the person or apartment you would like to contact. The classic system includes a one or two-line display that allows the visitor to scroll through a list of apartments. Once they select the apartment, they can push the call button to notify the tenant that they are in the lobby.The latest lobby intercoms include a large touch-screen panel. This multi-tenant intercom system provides a wireless connection from the lobby intercom station to an app on your smartphone.
ReplyDeleteAwsome blog, thanks for sharing.ISO 27001 Certification in UAE
ReplyDeletecomputer repair new jersey I have read all the comments and suggestions posted by the visitors for this article are very fine,We will wait for your next article so only.Thanks!
ReplyDeleteHome security is critical to you since you need to keep your family and your home liberated from hurt. Perhaps the main components of home security are keeping robbers from accessing your property.
ReplyDeleteThanks
Security and surveillance system
Wonderful article, Thank you for sharing amazing blog write-ups.
ReplyDeleteYou can also check out another blog on Cryptography and Network Security
I read your post, Great post with Nice information.Thanks for all the information.
ReplyDeleteA good way to say your words. Please also visit my site and let me know what do you think about my thoughts. Construction Site Security
ReplyDeleteA good way to say your words. Please also visit my site and let me know what do you think about my thoughts. Fire Watch Security Services
ReplyDeleteA good way to say your words. Please also visit my site and let me know what do you think about my thoughts. Security Services Edmonton
ReplyDeleteThis blog has valuable information, and the writer's written style is amazing. I want to appreciate it. Also, request the writer to write some more blogs on the Information Security Services for us. Thank You.
ReplyDelete