Demystifying Zero trust architecture

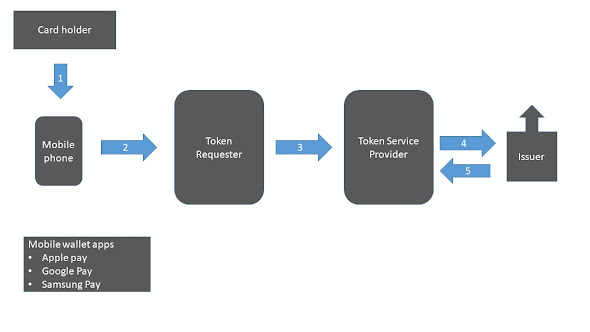
1. Introduction to zero trust: A more and more raging buzz word in the world of information security, Zero Trust Architecture refers to the “defense in depth” approach of implementing security concepts removing the process of automatically trusting actors and devices integrated in network. Zero trust architecture provides a thorough end to end approach to enterprise resource and data security controls interwoven around identity (person and nonperson entities), credentials, access management, operations, endpoints, hosting environments, and the interconnecting infrastructure. Zero trust leads to ultimately verifying every single component trying to connect to the system before granting access. Relying on fine grained methods such as micro-segmentation and granular perimeter enforcement based on users, zero trust helps to control security over controls such as trusting a user, machine or application for gaining access to a part of the enterprise network. Zero ...